Nerve Reconstruction after Trauma
Before: Young male who had a biking accident with facial fractures. Immediately after jaw surgery, he developed facial weakness.
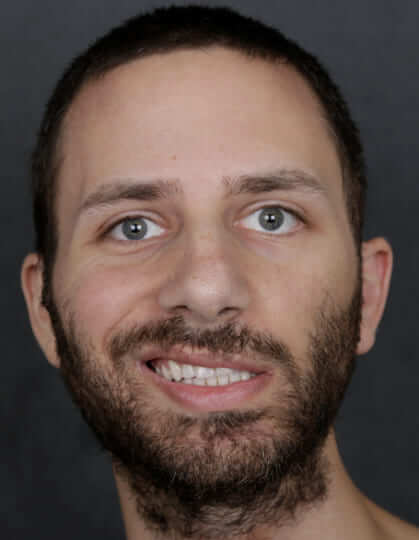
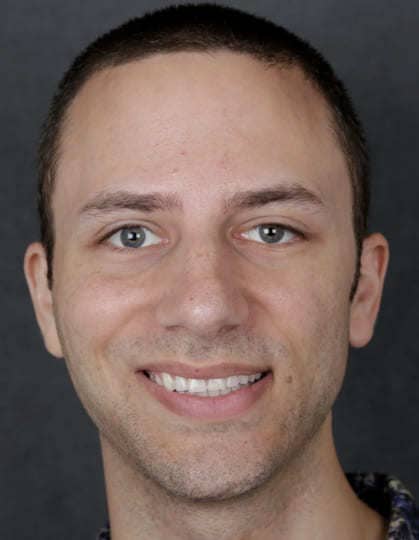


After: Surgical exploration showed a cut nerve. The nerve ends were sutured with a nerve graft. An eyelid weight was also placed to help to close the eye. 1 year after surgery with good eye closure, and smile.
Eyelid weight procedure to help close the eye
Before: Young male who had a biking accident with facial fractures. He underwent cheek bone and TMJ surgery in Europe and developed flaccid facial weakness.
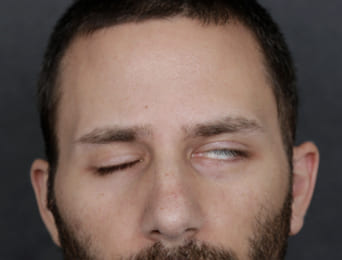
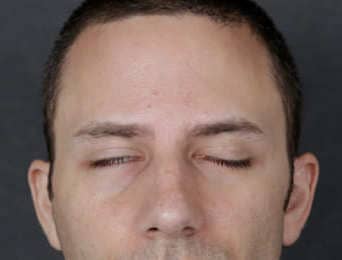
After: Surgical exploration showed a cut facial nerve. The nerve ends were sutured with a nerve graft. A platinum eyelid weight was placed to help to close the eye. His smile also returned.
Treatment of synkinesis (nonflaccid facial palsy) treated with surgical selective neurectomy
Before: Right sided Bell’s palsy with resultant synkinesis (frozen face).
Note tightness of face on right side.


After: Selective neurectomy of facial nerve branches with differential face lifting. Note, improved symmetry (right eye is more open, and lower face and smile is symmetric).
Nerve Reconstruction for Tumor
Before: Male with left acoustic neuroma and 3 year progressive facial weakness.
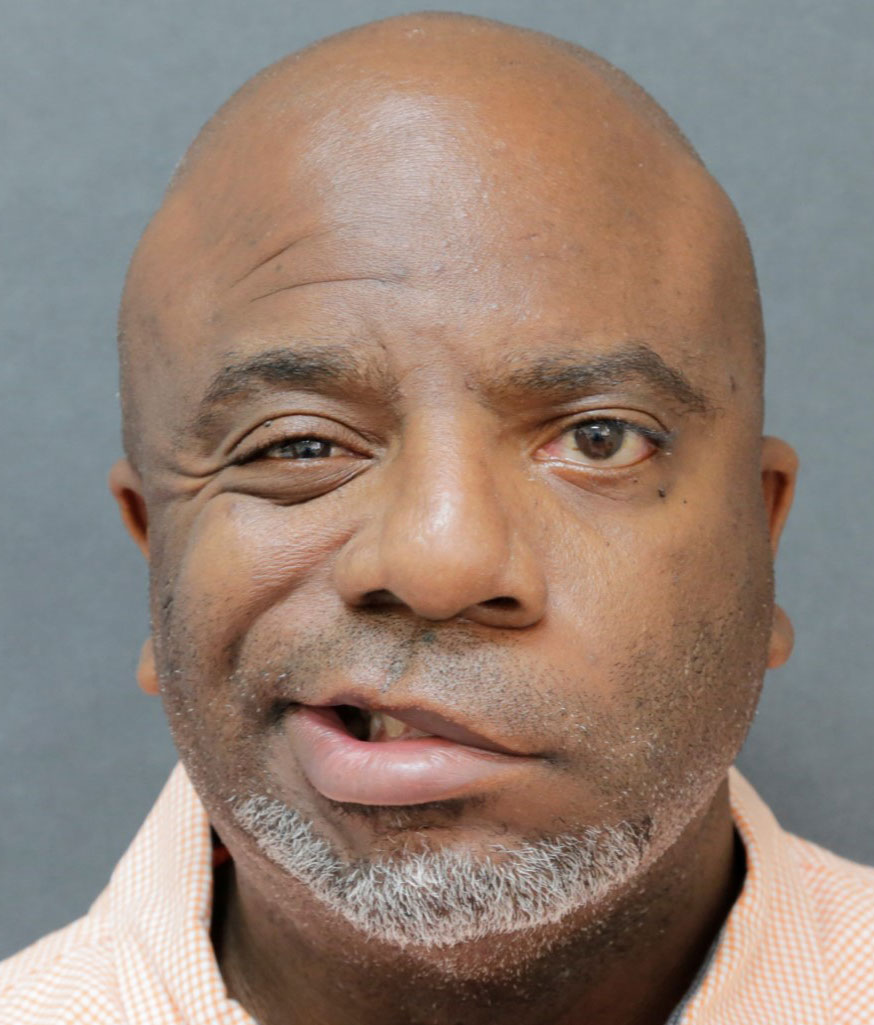
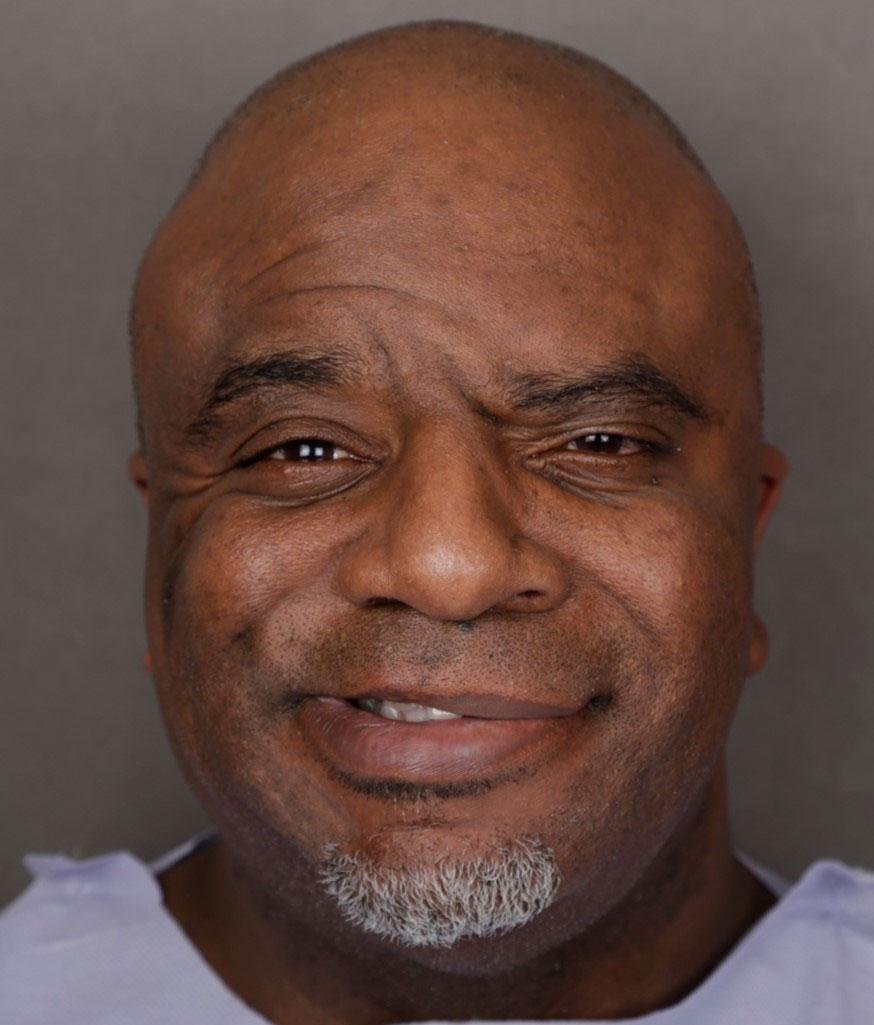


After: After nerve reconstruction: crossface sural nerve graft (gives spontaneous smile from the opposite side), hypoglossal to facial nerve trunk, and direct nerve to masseter(same side) to a left smile branch gives an early powerful smile. Also with fascia lata suspension for early lifting.
Eyelid weight procedure to help close the eye
Before: Unable to fully close the left eye.


After: After eyelid weight placement, now with full eye closure.
Eyelid weight procedure to help close the eye
Before: Left chronic flaccid facial palsy from acoustic neuroma. She is unable to close her left upper eyelid and cannot protect the eye.
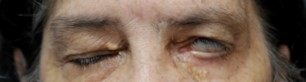
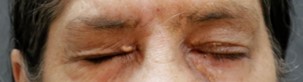
After: Symmetric eyelid closure after placement of thin profile platinum eyelid weight using eyelid crease incision.
Mucosal graft to the lower eyelid to lift the lower eyelid
Before: Young woman with laxity and retraction of the right lower eyelid and constant dry eye symptoms. She had right facial palsy from a brain tumor. Note the irritation/redness of the conjunctival (white) surface.
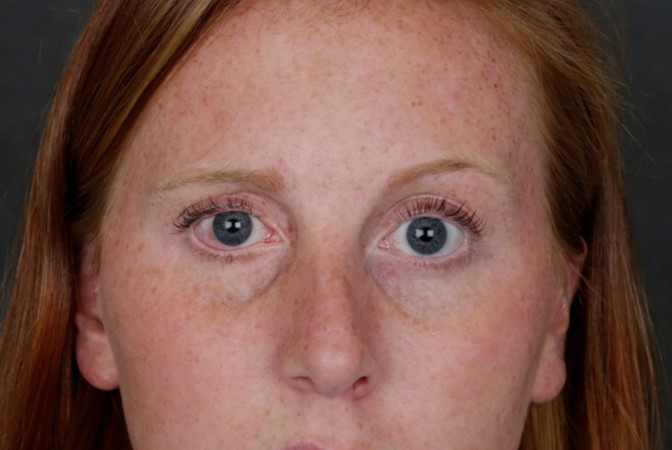
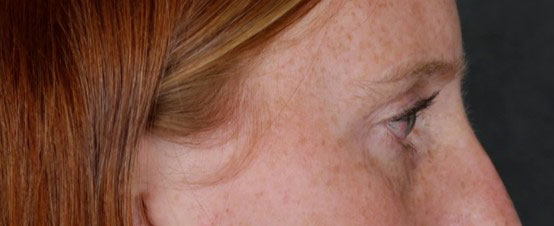
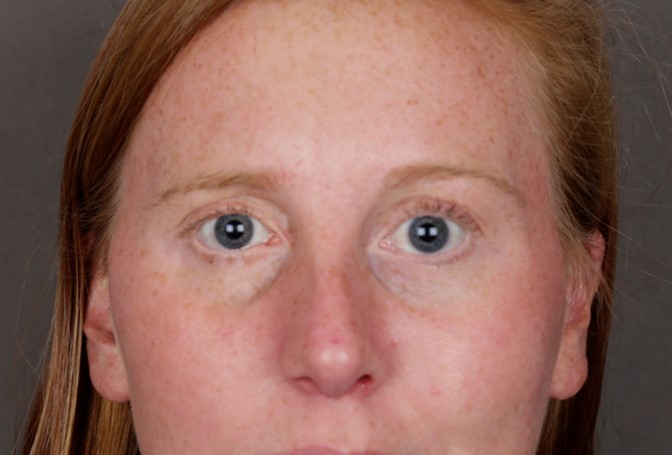
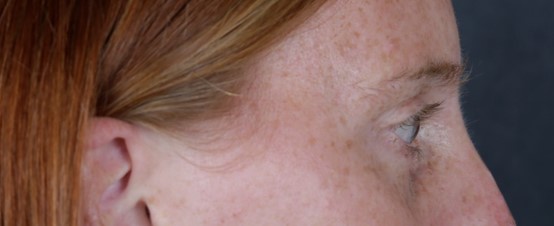
After: placement of palatal mucosal graft (tissue from hard palate of mouth) to the lower eyelid adds tissue and bulk to lift the lower eyelid upwards. Patient no longer has symptoms of dry eye and requires less frequent use of lubricating drops. She is very satisfied with the results.
Eye brow lift in flaccid facial paralysis
Before: Left brow ptosis/droop after sacrifice of left facial nerve during parotid cancer surgery.


After: After endoscopic brow lift and elevation of left nasal ala for midface symmetry. Patient also had gracilis muscle transfer for smile reanimation.
Treatment of congenital facial palsy Selective neurectomy with intraoperative facial nerve monitoring for lower lip smile symmetry
Before: Child with congenital right lower lip paralysis. The right lower lip does not pull downwards.
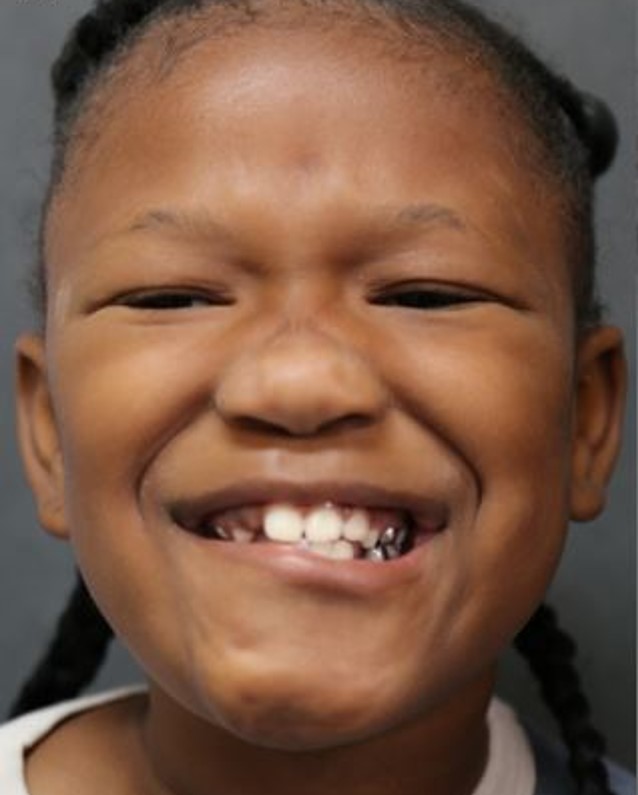
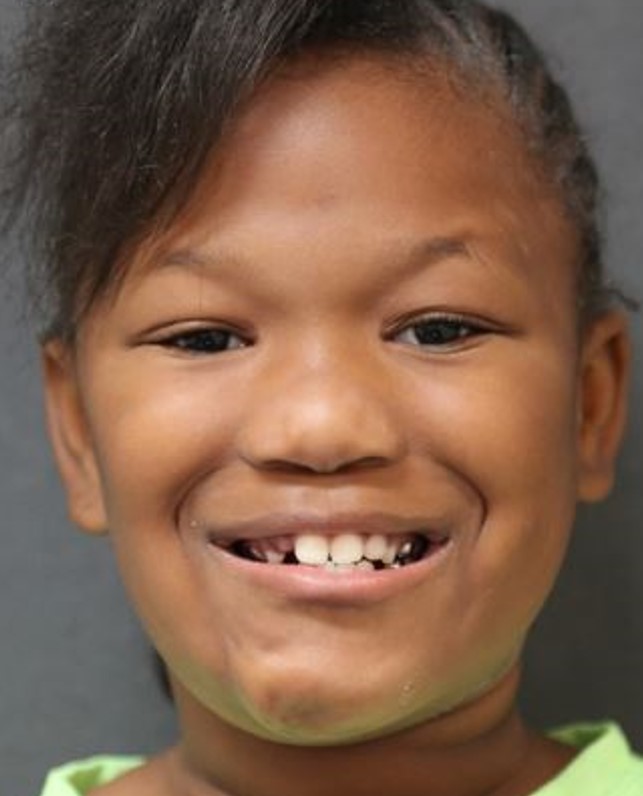


After: selective neurectomy of the left cervical branch with detailed nerve monitoring. Now, bilateral lower lips are symmetric. There is no change in speech or feeding.
Treatment of synkinesis (nonflaccid facial palsy) treated with botulinum toxin for facial symmetry
Before: Bell’s palsy with synkinesis of right face. This young lady had right facial flaccidity. After recovery, the right face became tight with less control of the separate facial muscles.
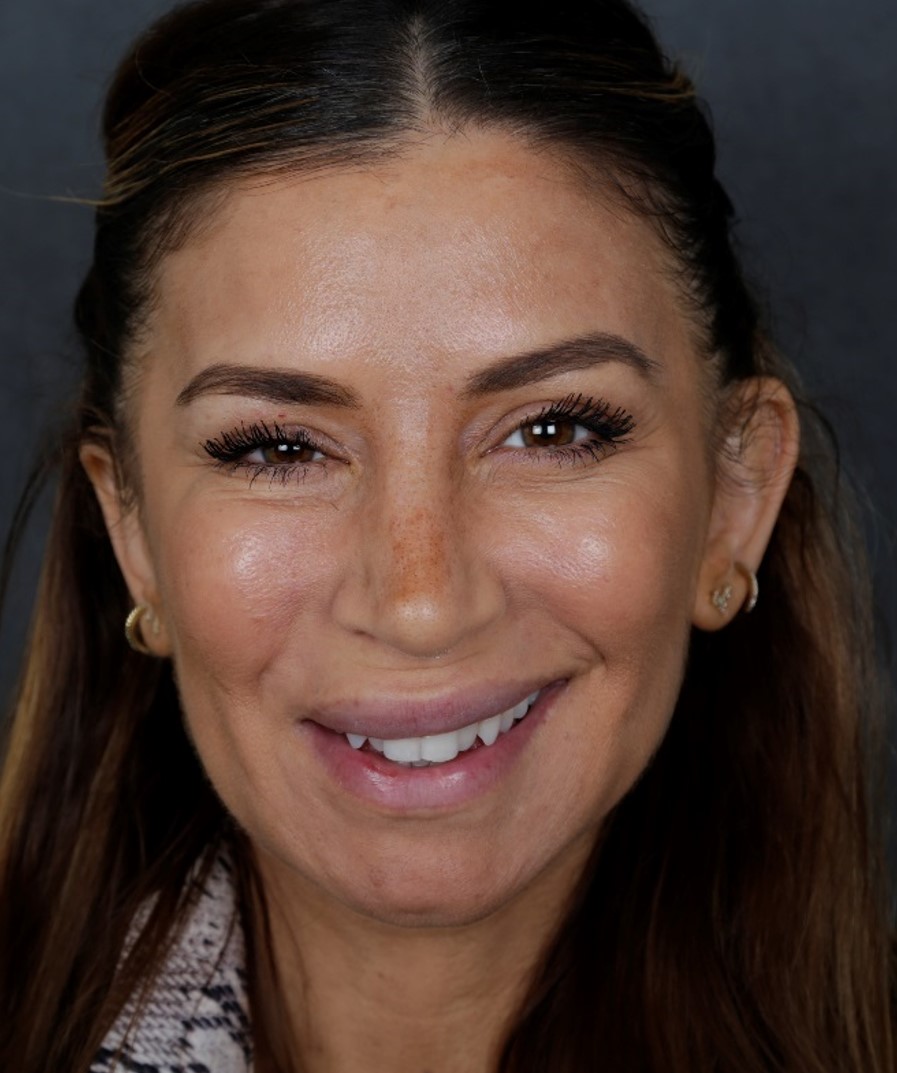
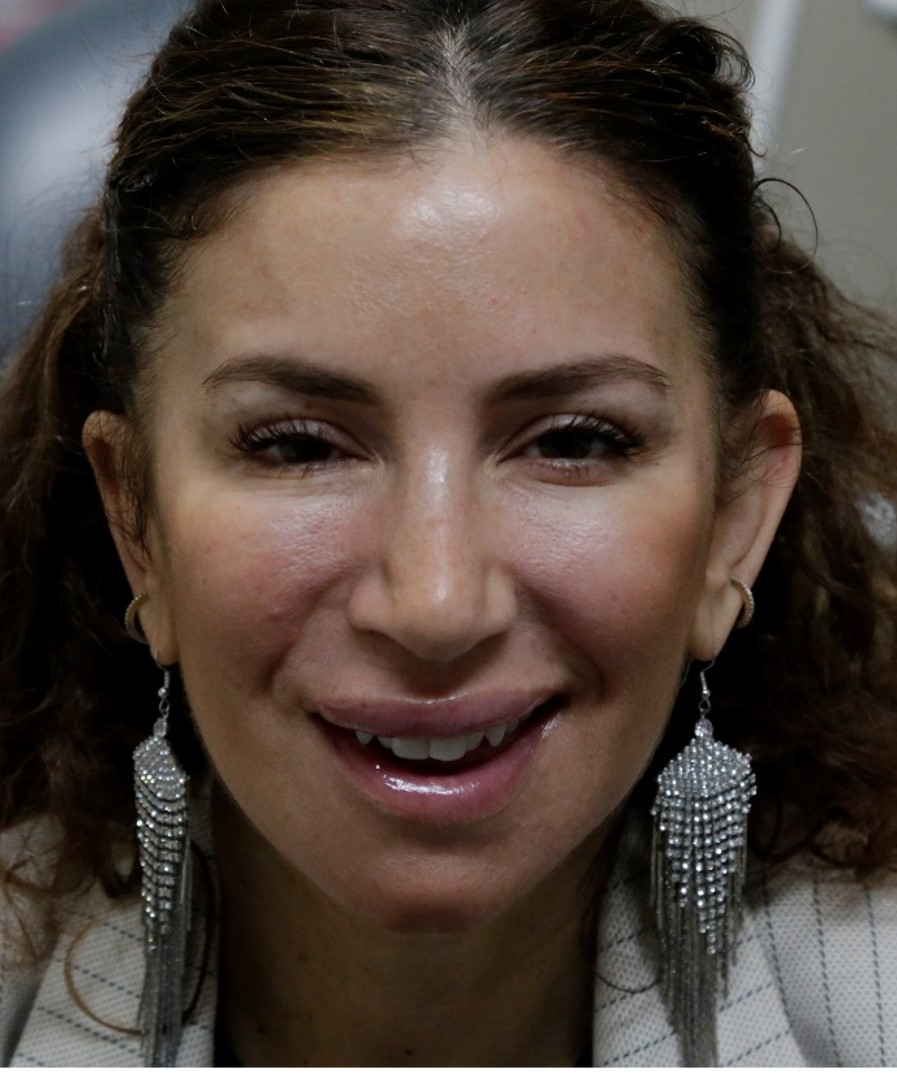


After: Improved symmetry after botox injections
(chemodenervation).
Treatment of synkinesis (nonflaccid facial palsy) treated with surgical selective neurectomy
Before: Patient with right facial synkinesis (tightness) and eye tightness after recovery from Bell’s Palsy. Notice how there is less white show of the right eye.
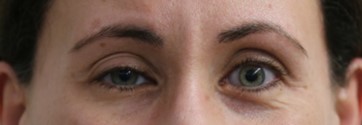
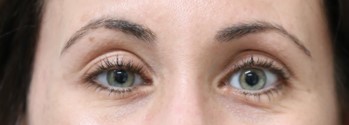
After: After selective neurectomy to branches to the right eye muscle. Now, the eye is more open.
Treatment of synkinesis (nonflaccid facial palsy) treated with surgical selective neurectomy
Before: Bell’s palsy with synkinesis of the left face.
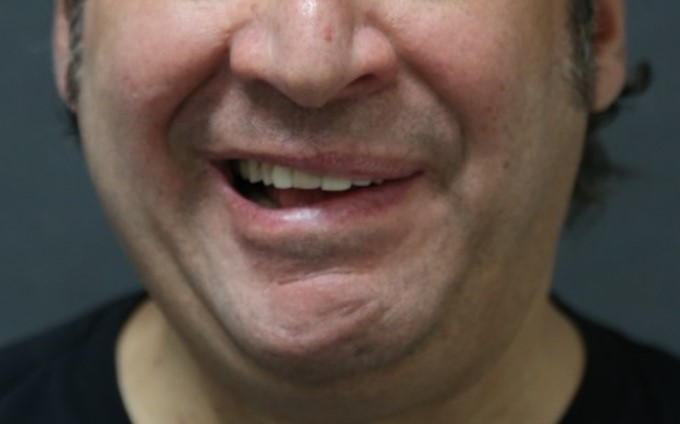
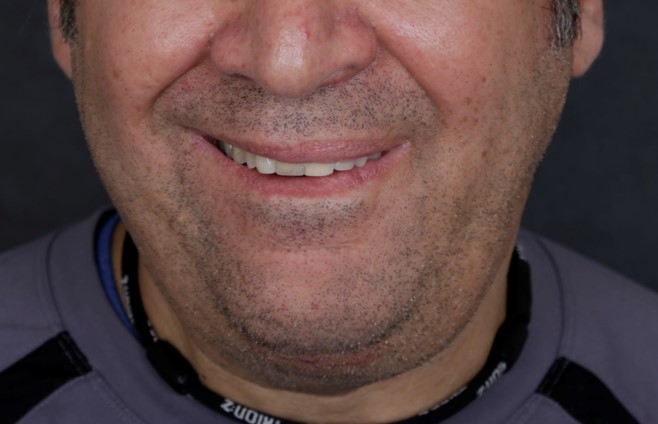
After: Selective neurectomy. Now, the left eye is more open, there is more lift of the left corner of the lip, and the lower lips and chin are more symmetric.
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Young girl with left midfacial flaccid paralysis. She had a lymphatic malformation removed from this area.
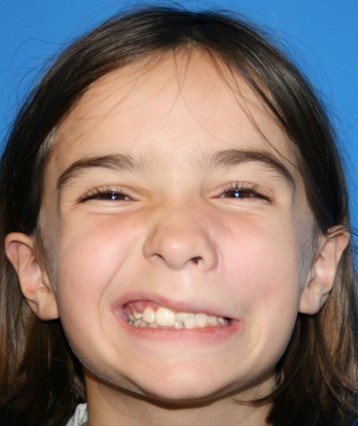

After: After 2-stage procedure with sural nerve graft followed by a gracilis muscle transfer to the left face. Now with dynamic, symmetric smile.
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Young boy with left flaccid facial paralysis after resection of a brain tumor (posterior fossa tumor).
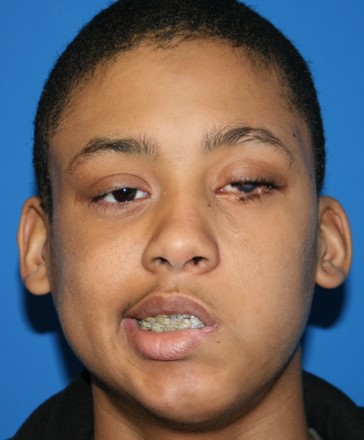

After: a two-stage reanimation surgery: sural nerve transfer followed by a gracilis free muscle transfer. Now with a dynamic smile.
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Teenage girl with right partial congenital facial paralysis, Notice that the corner of the right lip does not lift.
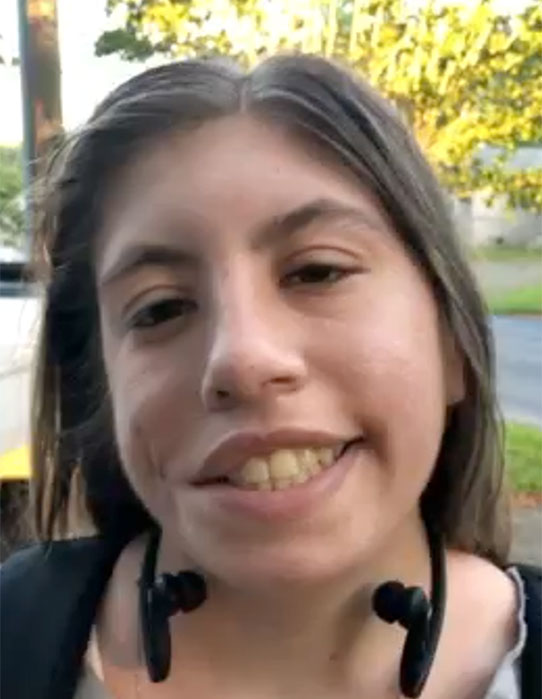
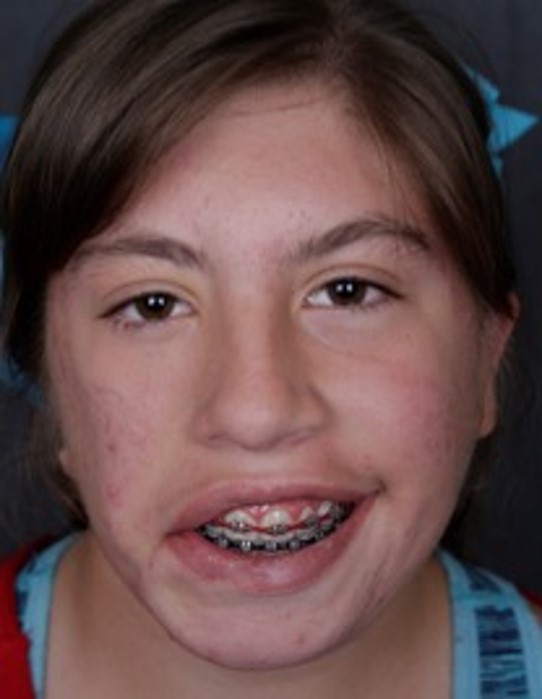

After: After one stage gracilis reanimation now with symmetric dynamic smile.
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Patient with micrognathia (underdeveloped mandible/jaw bone). Right facial weakness after previous jaw surgery.
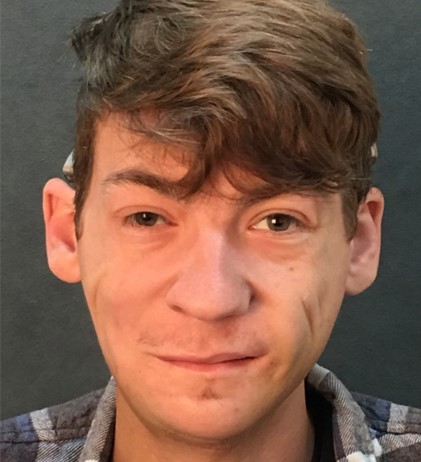
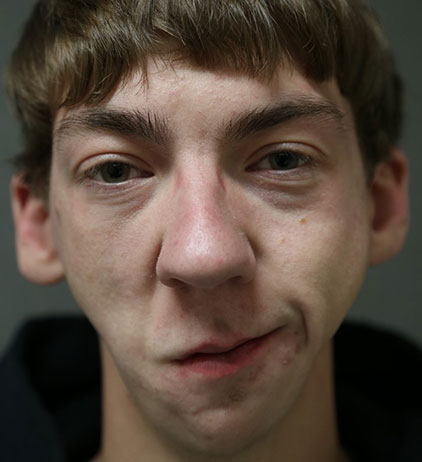

After: 2-stage surgery (sural nerve transfer followed by gracilis muscle transfer to the right face). Now, with symmetric smile. Patient also had bilateral jaw/mandible augmentation.
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Young girl with left facial paralysis and congenital lipomatosis.
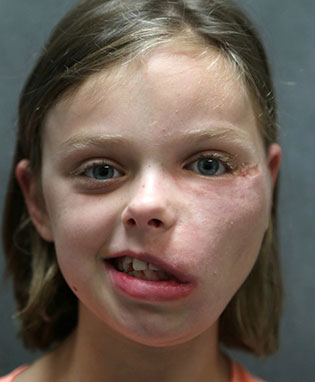

After: Reanimation with 2-stage gracilis free muscle and dual nerve input (the nerve to masseter and sural nerve were used as donor nerves).
Treatment of longstanding facial palsy: Muscle transfers Smile reanimation surgery.
Before: Bilateral facial palsy with bilateral tongue paralysis after surgery as a child.
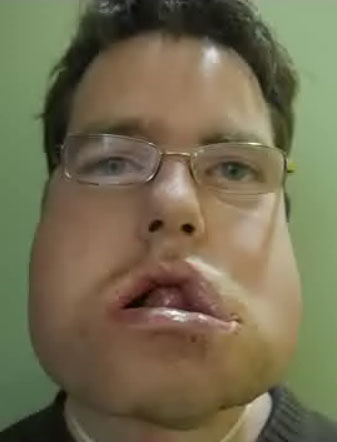

After: Simultaneous bilateral gracilis muscle transfer. Patient also underwent debulking of the malformation.
Protecting the facial nerve
Before: Child with cheek hemangioma in vicinity of the facial nerve. We use specialized intraoperative facial nerve monitoring and expertise to help to protect the nerve.
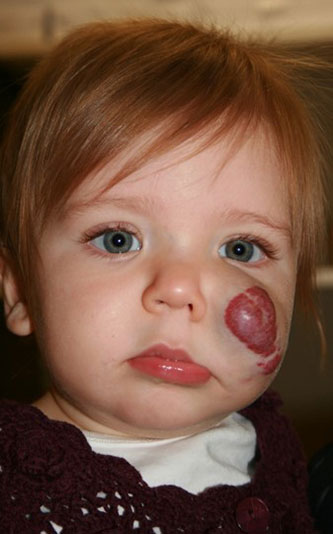

After: surgical excision of tumor with full function of facial nerve and imperceptible scar. We use intraoperative real time facial nerve monitoring (CMAP, continuous monitoring of the facial nerve)
